Overview of Part III
Part III is dedicated to future AutomationML applications and presents the results of selected research projects around AutomationML.
- Chapter 27 reports about how to efficiently develop mechatronic systems and how to efficiently solve the data exchange and consistency problem during the development workflow of production systems, taking various industrial tools and models into account.
- Chapter 28 reports about the application of the PPR concept and presents a pragmatic approach to managing dependencies and assessing the ramifications of changes using xQueries.
- Chapter 29 is dedicated to the Digital Twin and how to apply AML to integrate data and software into the Digital Twin over the lifecycle of a manufacturing cell.
- Chapter 30 is dedicated to the domain of climate protection and increasing energy efficiencythrough the use of an energy management system. A concept for the efficient engineering of technical energy management systems is presented, in which AutomationML is used at various points as a key technology.
- Chapter 31 investigates the usage of skills as a new abstraction layer for engineering and operating the future production plants. Skill-based engineering is a very new method that describes the individual components, constituting an automation system as objects with their respective services, named skills. It is a new level of engineering.
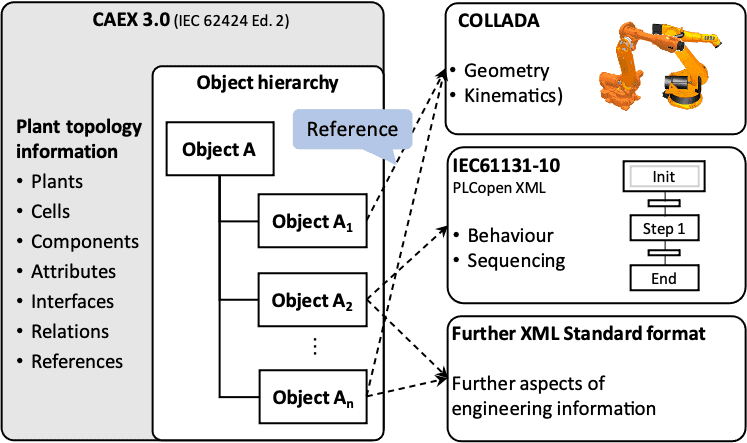
- Chapter 32 proposes a method for Engineering Data Logisticsbased on AML providing a discipline-crossing language concept to support the data exchange between a set of engineering tools within an engineering network, exploiting existing AML specifications for bilateral lossless data exchange.
- Chapter 33 describes the application of AML for energy simulations in the phase of virtual commissioning. AML helps to integrate different types of data into one organizational document and to interlink them. This linkage can be automatically created or supported by software tools, helping to reduce the manual effort. The concepts are validated by concrete commercial engineering tools.
Chapter 27
Birgit Vogel-Heuser, Minjie Zou, Michael Sollfrank (Technical University of Munich)
AutomationML based development of mechatronic systems
Chapter 28
Birgit Vogel-Heuser, Felix Ocker, Lukas Gehlen (Technical University of Munich)
Concept to refine and computationally evaluate PPR information in AutomationML
Chapter 29
Dominik Braun, Behrang Ashtari, Michael Weyrich (University of Stuttgart)
Integration of data and software into the Digital Twin via AutomationML
Chapter 30
Andreas Würger (Phoenix Contact Electronics GmbH)
Optimizing the engineering of technical energy management systems
Chapter 31
Milan Vathoopan (TU Munich), Kirill Dorofeev (fortiss GmbH), Alois Zoitl (Johannes Kepler University Linz)
Skill-Based Engineering of Automation Systems: Use Case and Evaluation
Chapter 32
Arndt Lüder (Uni Magdeburg), Stefan Biffl, Felix Rinker (TU Wien), Anna-Kristin Behnert (Uni Magdeburg)
Engineering Data Logistics based on AML
Chapter 33
Jannis Sinnemann, Matthias Bartelt (Ruhr-Universität Bochum), Anton Strahilov, Dimitri Penner (EKS InTec GmbH), Bernd Kuhlenkötter (Ruhr-Universität Bochum)